Rapid Alloy Development Techniques for PBF-LB: Systematic study of microstructure formation during AM for Ni-base superalloys
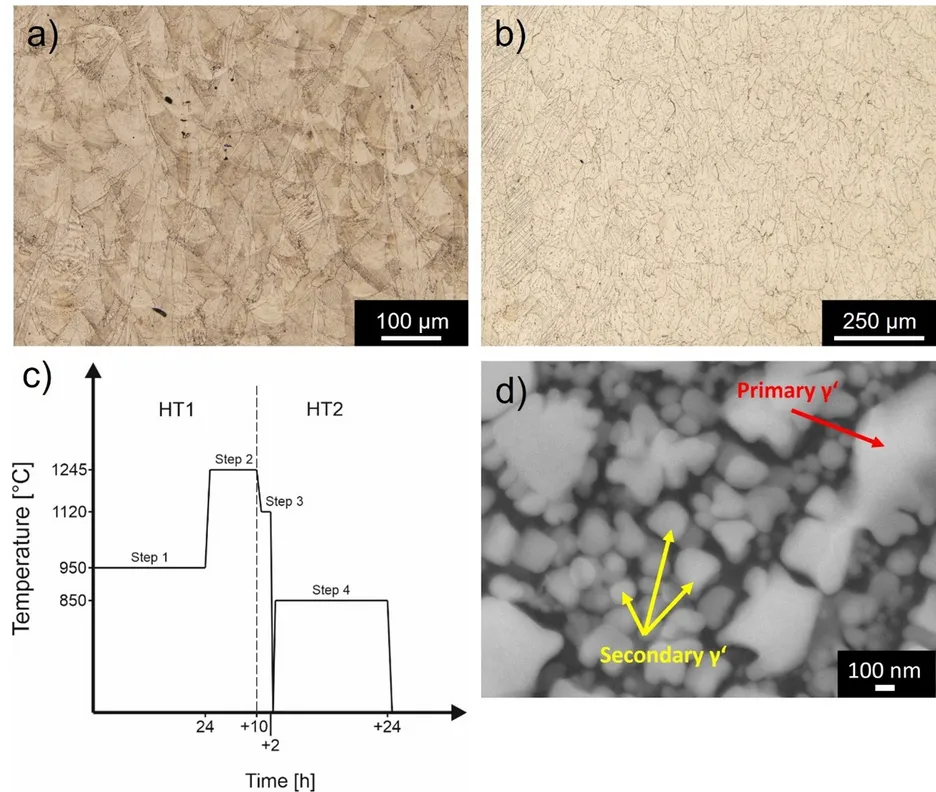
The RapidNibas project focuses on the accelerated development and optimization of nickel-based superalloys for additive manufacturing using laser powder bed fusion (PBF-LB/M). At the center of this research is a special alloy developed by Oerlikon, known as MetcoAdd 738 LC-A, which is based on the well-established IN738LC alloy. This material is typically used in high-temperature applications, such as in aircraft or gas turbines, and is characterized by its excellent oxidation resistance and creep strength at elevated temperatures.
Although PBF-LB/M offers numerous advantages for producing complex geometries, components made from MetcoAdd 738 LC-A exhibit significant limitations in mechanical properties after the printing process. These shortcomings are primarily due to a undesired grain structure and a non-ideal precipitation of the Ni₃(Al,Ti) γ′-phases (gamma prime), which are crucial for maintaining the alloy’s strength at high temperatures.
Key Objectives:
The goal of RapidNibas is to systematically address these issues through targeted post-processing, especially heat treatments. Within the scope of the project, various parameter combinations are being investigated to enlarge the grain size and to enable controlled precipitation of the γ′-phases. This tailored microstructural adjustment is expected to lead to significantly improved mechanical properties, ensuring that the alloy meets the performance requirements for high-temperature applications after additive manufacturing.